Dendoderma mite disease is also known as folliculosis or fat mite disease. It is a common and stubborn skin disease in dogs caused by the parasite of the sebaceous glands or hair follicles. It is often found in puppies aged 5-10 months.

1. The causes of dog demodex disease:
1. The dog demodex is translucent and milky white, with a narrow and long body like a worm, with a length of 0.25-0.3 mm and a width of about 0.04 mm. It can be distinguished from the appearance: front, middle and rear parts.
2. The entire development process of dog demodex mite is carried out on the dog body, including eggs, larvae, nymphs, and adults, among which nymphs have 3 stages.
3. Dog Demodex mites mostly parasitize in the upper part of the diseased skin hair follicles, and then turn to the bottom, rarely parasitize in the sebaceous glands. In addition to being parasitized in hair follicles, it can also live in the tissues and lymph nodes of dogs, and some of them are reproduced in it.
2. Clinical symptoms of dog demodex disease: The symptoms of dog demodex can be divided into two types:
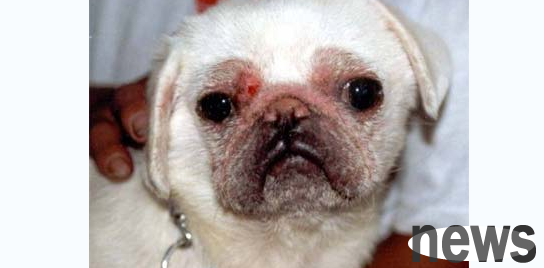
1. Scale type: Mostly occur in the eyelid and its surroundings, corners of the mouth, forehead, nose, lower neck, elbows, toes, etc. Hair loss in the affected area is accompanied by mild flushing of the skin and silver-white sticky dandruff, which makes the skin appear slightly rough and cracked, or has small nodules. Later, the skin turned blue, grayish white or red and coppery, and the affected area was almost itchy, and some remained unchanged for a long time. Some turn to pustule type.
2. Pustular type: It occurs frequently on the neck, chest, inner side of the Yin and other parts, and later spreads throughout the body. Large areas of hair loss on the surface of the body, large areas of erythema, thick skin, and often become wrinkles. There are diffuse pustaceous from millet to wheat grains. The pustaceous pustaceous is blue-red and discharges pus when squeezed. It contains a large amount of demodex and eggs. After the pustaceous ulcers form, it will cause ulcers and cause an unpleasant odor. The pustule type has almost no itching. If there is a severe itch, it may be a mixed infection. You may eventually die of failure, poisoning, or sepsis.
3. Prevention and control measures for dogs:
1. Isolate and treat sick dogs, and use acaricidal drugs to disinfect contaminated places and utensils.
2. In addition to local pesticides for severely ill dogs, antibacterial drugs should also be used throughout the body to prevent secondary infection.
3. For scale type, the affected area should be scrubbed with an equal amount of alcohol or ether, or scraped it with it so that the drug can reach the hair follicles. The medication is as follows: 25% or 50% benzoate benzoate emulsion, apply thoroughly to the affected area: 5% formalin solution in soak for 5 minutes, once every 3 days, a total of 5-6 times.
4. Pustules type, first cut the pustules, wash them with 3% hydrogen peroxide solution, apply them with 3% iodine tincture or 3% gentian purple solution, and then treat them according to scales.
5. Demodex mites are parasitic in the skin and subcutaneous connective tissue. It can also be parasitized in the lymph nodes, so when treating pustule type, local therapy and chemotherapy must be used (intravenous injection of papan blue or intramuscular injection of coniferin, etc.), and supplemented with large doses of penicillin therapy.